This Dalmatian’s Unique Size Is Due to Dwarfism in Dogs—Here’s What That Means
A Dalmatian called Dino has become an Internet sensation for his unique condition – dwarfism. Dino’s mom posted a video on TikTok revealing how she got a Dalmatian without knowing that he has dwarfism, achondroplasia to be exact, and now he has become incredibly popular online as well as in real life. (watch TikTok video below)
The video has gone viral on the platform, garnering over 2 million likes. In addition, the TikTok account, @dino.and.ruby has 375.5K followers. Dino’s parents post videos of their dwarf Dalmatian and of Ruby, a rescue Beagle.
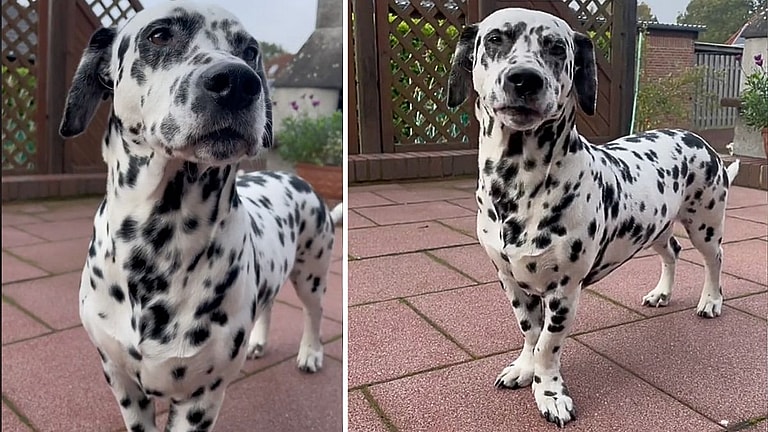

Dino Is A Cute And Healthy Dog
Dino lives in Hamburg, Germany, with his two moms and fur sister Ruby. One of his moms has shared his story on social media, detailing how they adopted the dog from a family in Germany. Despite his short height, she claims that Dino is a completely healthy and happy 7-year-old dog who loves chicken and spending time with his sister, Ruby.
In addition, Dino gets a lot of attention due to his size whenever he goes on walks. People love to snap pictures of him and kids often shout “Marshall” upon seeing him, referring to the Disney character from PAW Patrol.
@dino.and.ruby No more pup-arazzi 📸 😆 #dalmatian #dwarfism #fyp #dog #popular #trending ♬ Popular – From "Wicked" Original Broadway Cast Recording/2003 – Kristin Chenoweth
The TikTok video’s comments suggest that many people think he is not a purebred Dalmatian and is actually bred with a smaller dog, for instance, a Corgi. A user, Nicole, writes, “Are you sure he’s not just mixed with a corgi? Lol” However, Dino’s mom explains that their furbaby is tested, and was diagnosed with chondrodysplasia, which is a type of dwarfism.
Want to know more about the rare condition of dwarfism in dogs?
Dwarfism In Dogs: What Is It?
If you are unsure about whether dwarfism exists in dogs, the answer is yes, it does. As per Dr. Zach Coston, a veterinarian, “Dwarfism in dogs can cause both relatively benign, aesthetic issues such as a larger than normal head and more severe issues that impact their quality of life like spinal deviations.”
What Are The Types and Causes of Dwarfism in Dogs
You might be wondering now, “What causes dwarfism in dogs?”. Veterinarian Dr. Pathy Khuly cites two types of dwarfism in dogs—achondroplasia and pituitary dwarfism—as common causes of the condition.
Achondroplasia in Dogs
Dino the Dalamatia is diagnosed with this type of dwarfism. Dr. Khuly says, “The most common version of dwarfism in dogs is achondroplasia — a condition also observed in humans. Achondroplasia in humans is caused by the genes that encode for growth factor receptors in a cell type known as a fibroblast.” The precise genetic location in dogs is unknown to the researchers for now, but they have observed a similar genetic mutation in breeds like corgis and dachshunds, which have limbs of disproportionate short size.
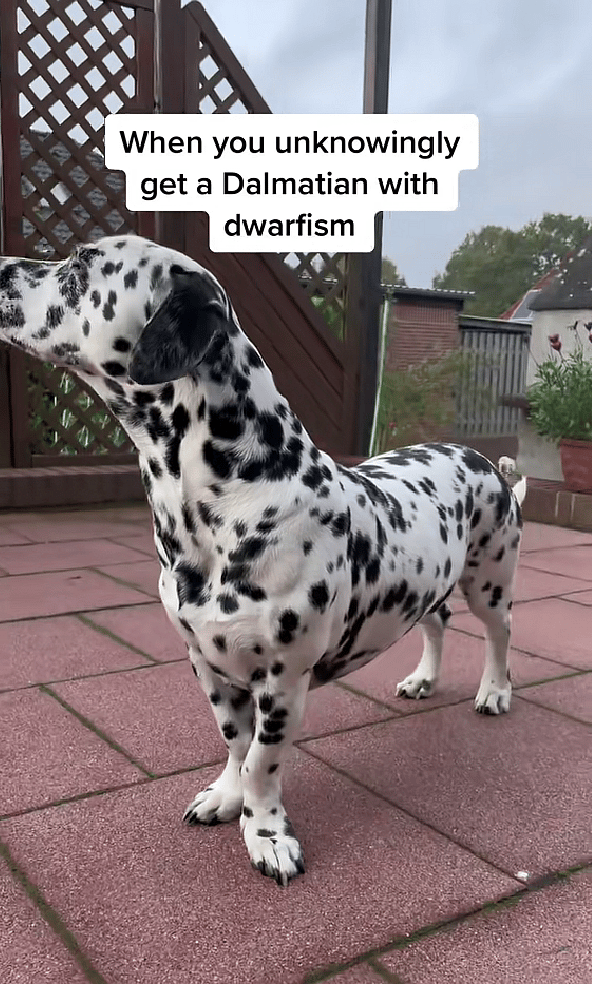

Dr. Coston states, “Dogs with achondroplasia are affected with a disproportionate skeletal dwarfism in which their bones do not grow to the normal size that is conventional to their breed.”
Achondroplastic dwarfism in dogs is also known as skeletal dwarfism, disproportionate dwarfism, chondrodysplasia, or osteochondrodysplasia, reflecting the condition’s impact on bones and cartilage.
Pituitary Dwarfism in Dogs
Another name for juvenile-onset panhypopituitarism, pituitary dwarfism “is most commonly caused by a failure of the pituitary gland to develop in utero, resulting in a lack in production of trophic hormones responsible for the growth and function of certain endocrine cells,” according to Dr. Coston. Consequently, the dog doesn’t possess the growth hormone and ends up being dwarfed.
Dr. Coston also adds, “Pituitary dwarfism in dogs can also be caused by benign brain tumors that affect the pituitary gland, leading to lower levels or the complete absence of growth hormones.”
Symptoms of Dwarfism in Dogs
Dwarfism in dogs can have different symptoms depending upon the type of dwarfism they have. Let’s take a look below.
Achondroplasia
Achondroplasia dwarfism in dogs typically exhibits the following characteristic physical features:
- Corkscrew-shaped tails
- Bowed legs and limbs – especially in the front legs
- Enlarged joint structures
- Misaligned, crooked teeth
- Shorter nasal passage
- Undershot jaw alignment
- Larger than average head size
Disproportionate dwarfism in dogs may also result in a range of associated health issues, which can vary in severity. Some may develop more profound complications, including:
- Spinal abnormalities such as spina bifida, spinal deviations, and hemivertebrae
- Brachycephalic syndrome
- Angular or rotational limb deformities
- Intervertebral disc disease
These conditions can significantly impact the dog’s quality of life, making it essential for owners to work closely with veterinarians to manage their pet’s health.
Dr. Khuly asserts, “In some breeds, these diseases are inherited by design, while in others, the mutation occurs more sporadically. In this latter group, the additional problems associated with achondroplasia are often more severe.”
Pituitary Dwarfisms
Pituitary dwarfism in dogs typically manifests around two months of age, halting normal growth and development. Despite reaching skeletal maturity at approximately four years old, affected dogs often face a range of challenges, including:
- Hormonal deficiencies leading to hair loss and dental issues
- Impaired adult dentition development
- Other issues specific to the individual dog’s hormonal imbalances
Unfortunately, pituitary dwarfism is often associated with a shortened lifespan, making it a particularly concerning condition for affected dogs and their pet parents.
Health Problems Caused By Dwarfism
Dogs with achondroplasia-related dwarfism typically don’t have a significantly shorter lifespan, but they are more prone to developing various health issues related to their condition. This can significantly impact their:
- Mobility
- Respiratory function
- Comfort level
- Dog’s overall quality of life
In contrast, dogs with pituitary dwarfism, such as German Shepherds, are more severely affected. They often have a markedly shorter lifespan and require management of associated hormonal conditions, including:
- Addison’s disease
- Hypothyroidism
These conditions require prompt treatment to ensure the dog’s comfort and well-being.
Treatment of Dwarfism In Dogs
Achondroplasia in dogs is generally associated with a relatively mild impact, with fewer and less severe adverse effects compared to pituitary dwarfism. “Depending on how severe the achondroplasia is, anti-inflammatory medication or pain relievers may be used to ease any discomfort your dog is experiencing,” notes Dr. Costa.
However, it’s essential to consult with a veterinarian to assess the severity of your dog’s achondroplasia and determine the best course of action. With proper support and care, dogs with achondroplasia can lead happy and healthy lives.
For pituitary dwarfism, your veterinarian may recommend one of the following treatment options:
1. Hormone Supplementation
Your vet may prescribe hormone supplementation to manage secondary hypothyroidism associated with pituitary dwarfism. Close monitoring is crucial during this process. Additional medications like growth hormones or megestrol acetate (synthetic progesterone) may be used to stimulate growth hormone release from your dog’s mammary tissue.
2. Surgery
According to Dr. Costa, “If the pituitary dwarfism is the result of a tumor, surgery may be an option as long as the tumor is not in an especially vital and delicate area.” However, your vet may not recommend surgery if the chances of successful recovery are low.
Dwarfism In Dogs Pictures
Here are some other dogs living with dwarfism:
1. Puquenina
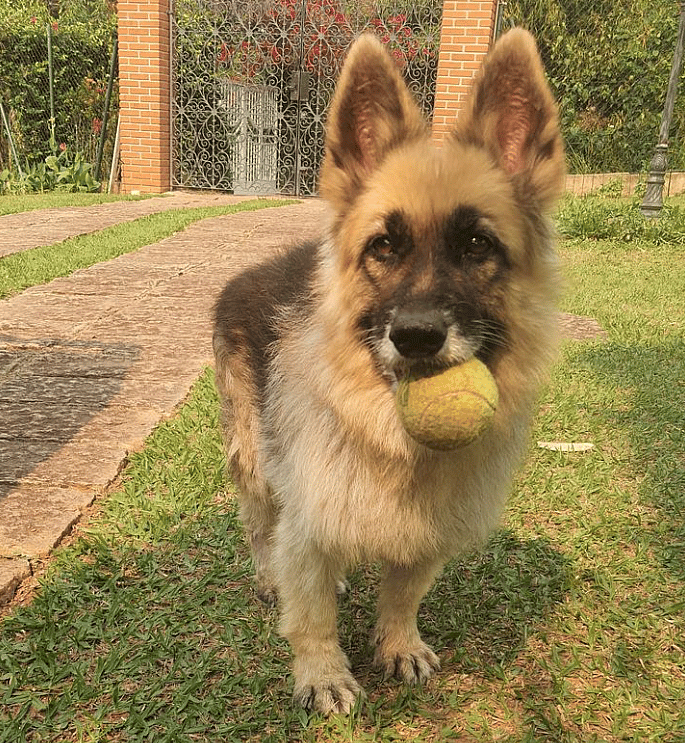

Puquenina (@puquenina) is a beautiful German Shepherd dog who is a dwarf. His nickname is Puque and seems to have a happy and healthy life.
2. Moose
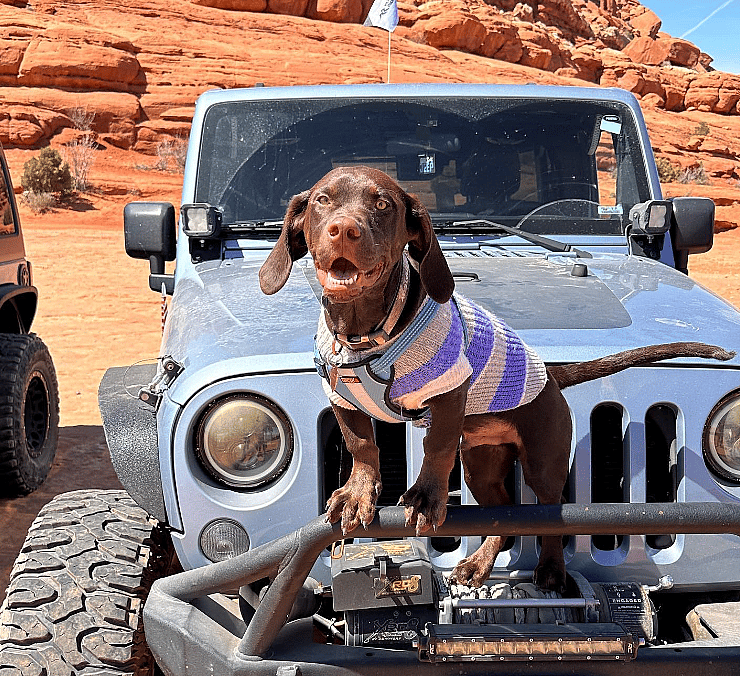

Moose (@dwarfjeepdog) is a dwarf Labrador Doberman mix dog, whose color is a gorgeous chocolate. With a cute underbite, he accompanies his pet parent on adventures in their Jeep.
3. Cooper
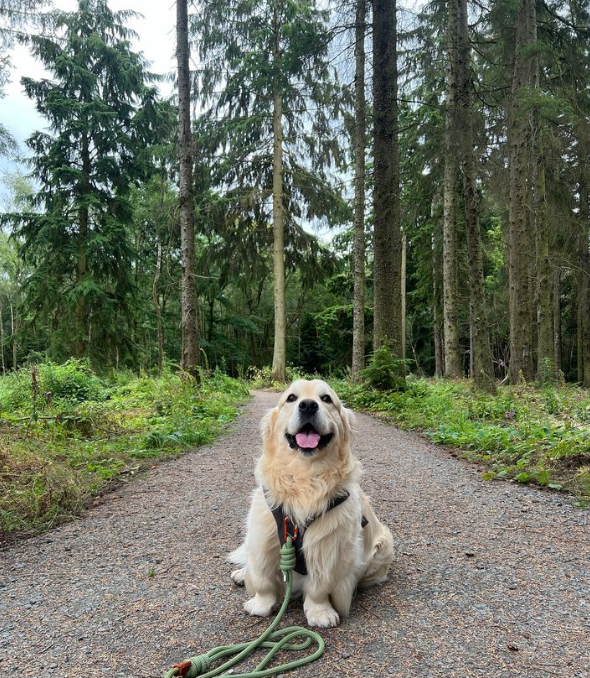

A Golden Retriever (@coopersjournal) named Cooper didn’t grow to the normal size. The four-year-old dog tested negative for dwarfism, but his unusually short legs are one of the clinical signs of dwarfism.
4. Fiadh
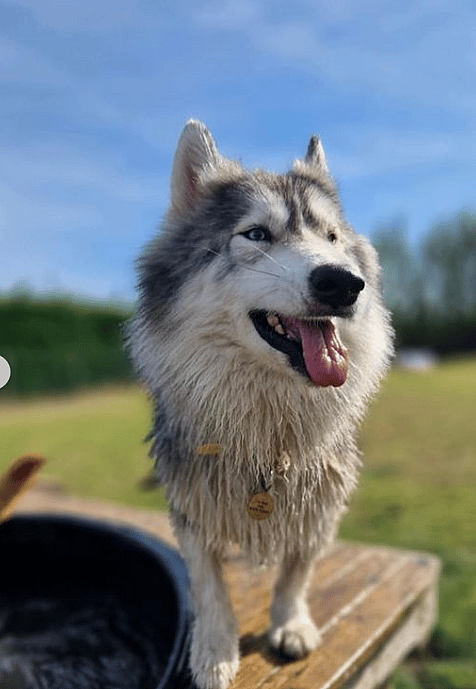

Fiadh (@thedwarfhusky) is a Husky with dwarfism condition. Deaf and partially sighted, Fiadh is a rescue dog.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How common is dwarfism in dogs?
Achondroplasia, a form of dwarfism, is remarkably common in dogs, as many breeds have been selectively bred for this characteristic. In contrast, pituitary dwarfism is an extremely rare condition, with German Shepherds being the most commonly affected breed.
Does bowed front legs mean dwarfism in dogs?
Bowed front legs are a common symptom of achondroplastic dwarfism in dogs. However, to be sure, you need to get a veterinary appointment and get your dog tested for the condition.
What is the life expectancy of dwarfism in dogs?
Achondroplasia doesn’t have any direct correlation with affecting a dog’s life expectancy. It can only impact their quality of life. On the other hand, pituitary dwarfism is a severe type of dwarfism and this condition generally means a shorter lifespan for the dog than normal depending upon the breed.