Why Your Dog Is Dragging Their Bum on the Floor, According to Experts
I’m guessing you’ve landed here because your pup has been sliding his backside across the floor a little too often — also known as scooting — and you’re wondering what might be causing it.
Seeing your dog scooting, be it on your living carpet, kitchen floor, lawn……you name it, can be amusing to watch. But best believe, your dog has a valid reason for doing so — and this reason has nothing to do with them trying to entertain you. (Watch Video Below)
Scooting is your dog’s attempt to find relief from the pain they’re experiencing as a result of an underlying anal gland issue. So, as a dog owner, you should take scooting as a sign that your pup needs to see the veterinarian as soon as possible.
@senior.dogs Its not funny it's a sign to check you pups anal glands #pethealth ♬ 오리지널 사운드 – Rude V 루드비
What Exactly Are Dog Anal Glands?
Also referred to as anal sacs, anal dogs in dogs are simply two small, oval-shaped sacs (with openings) that are each located inside the left and right side of a dog’s anus.
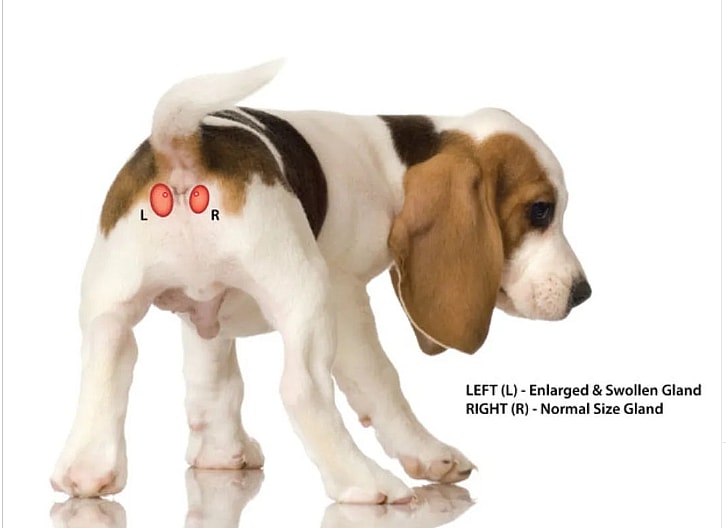
Each anal gland often contains a brown, fishy-smelling fluid that’s naturally emptied whenever your dog poops. As stool passes through your dog’s anus, it presses onto the anal glands, which then secrete the strong-smelling fluid. This brown fluid acts more like a lubricant as your dog poos.
Moreover, our canine friends involuntarily excrete this pungent fluid when they’re frightened or stressed out.
If your dog has issues with their anal glands, they’ll have a build-up of this smelly fluid in their glands. “Every time dogs poop, the pressure of the stool and contracting muscles expel a small amount of the smelly material inside the glands. If the anal glands do not empty properly, they can swell up and become uncomfortable,” explain experts at the Critters Veterinary Center.
Causes and Signs of Anal Gland Issues in Dogs
Typically, anal gland issues arise due to blockage in the anal glands, which means your dog’s glands are unable to secrete the smelly fluid as they normally would.
Various factors can cause this anal gland blockage, among them obesity, infection around a dog’s anus, abnormal bowel movement (hard or soft stool), external parasites on the rear area, and lack of enough fiber in their diet. Impacted anal glands can cause great discomfort for your dog and, if left untreated, can become severely infected and cause unbearable pain.
“Usually, the anal sacs content are liquid and can easily be expressed manually (glove, lube, finger). Sometimes, the contents will dry out into a gritty clay consistency, which is almost impossible to express manually and causes pain doing so. In my experience, these dogs are most prone to developing an anal gland abscess with Fistula,” explained Dr. Magda Upton (BSc BVMS) in an Instagram post.
In other words, the longer your dog’s blocked anal glands go without getting emptied, the more the fluid trapped inside continues to thicken (and can rapture).
In severe, recurring cases, anal gland impaction or infection will progress to anal gland abscess, and your dog may need surgery to resolve the issue.
“My dog had constant abscesses from impacted anal glands. Getting them removed improved her quality of life so much. Those abscesses cause severe pain. There can be side effects from the surgery, like incontinence. My dog did not have any bad side effects,” wrote user @ Ill-Parsnip2657 in a Reddit discussion on anal gland impaction in dogs.
Like most dog owners, you’ve likely found yourself having thoughts such as “How to tell if anal glands are full,” or “What are the symptoms of anal gland blockage in dogs?” Well, here are seven common symptoms of blocked anal glands in dogs:
- Excessive scooting
- A pungent fishy odor in their rear area
- Constant licking of their rear area
- They seem to strain while pooping
- Hesitance to sit down
- Redness/blood/ discharge/pus around their anal area
- Whimpering when defecating or when their rear end is touched
Treatment of Blocked Anal Glands in Dogs
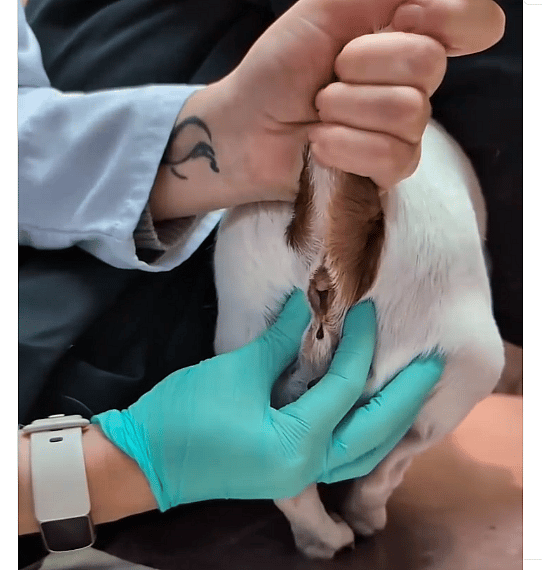
In most cases, mild anal gland issues in dogs are resolved by manually expressing these swollen sacs to flush out the trapped liquid. If your dog has severe anal gland infection, the vet will likely put them under anesthesia before expressing the full glands.
While some pet parents are able to do the emptying at home, you should never attempt to express your dog’s impacted anal glands manually if your vet hasn’t instructed you to. Doing so can cause further complications, which will only put your dog in more pain.
“It is important to note that anal gland expression should be performed by a trained professional, such as a veterinarian, vet technician, or groomer, as improper technique can lead to injury or infection. If you suspect your dog has anal gland issues, or they are showing signs of discomfort, consult with your veterinarian for an appropriate evaluation and treatment plan,” advises Dr. Kristi Crow of City Way Animal Clinic Fountain Square.
So, if your mind is flooded with thoughts such as “how to express dog anal glands,” “expressing your dog’s anal glands,” “dog anal gland expression,” “how do you squeeze a dog’s anal glands,” or anal gland expression near me,” remember: it’s best to always speak to your vet first so they can advise you accordingly.
If you’re curious about how anal gland expression is done, check out the video below:
@theswiftiekittens Anal gland (sac) expression in a dog. #tiktokpartner #learnontiktok #analglandexpression #dog #vetmed ♬ Rubber Ball – Chris Alan Lee